China’s Population, the world’s second-largest economy, grapples with a significant challenge as new data reveals a second consecutive year of population decline. The figures, released on Wednesday, indicate a population of 1.409 billion at the end of 2023, reflecting a notable decrease of 2.08 million from the previous year. This decline, double that of the preceding year, sparks concerns about the future growth of the economic powerhouse.
Factors Contributing to Decline: Urbanization and Low Birth Rate
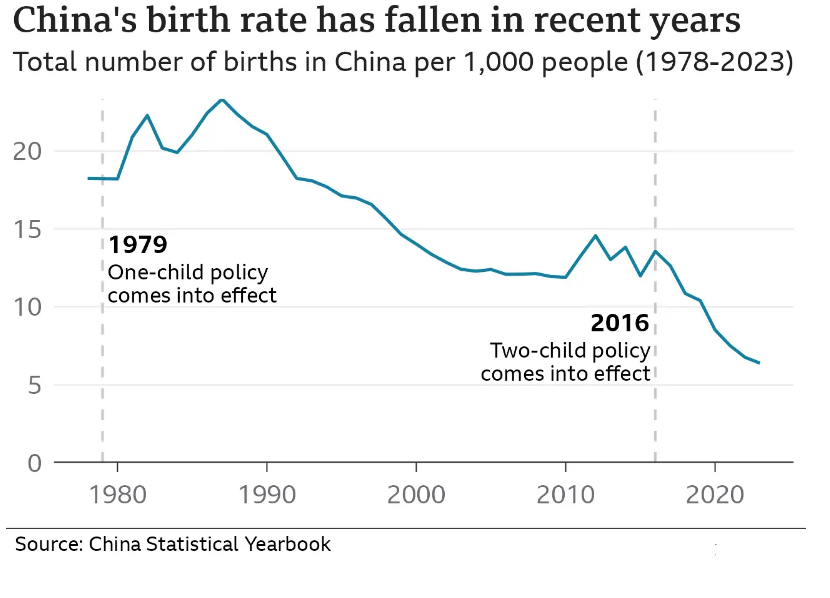
Experts attribute the decline to the country’s expanding urban class and a record-low birth rate. Beijing disclosed that the birth rate has now reached 6.39 per 1,000 people, aligning with other advanced East Asian nations like Japan and South Korea. China’s population has witnessed falling birth rates for decades, a trend initiated by the controversial one-child policy imposed in the 1980s to address over-population concerns.
Policy Shifts: Attempts to Reverse the Trend
In 2015, the Chinese government lifted the one-child policy in an effort to counter the declining population. Subsequent measures included incentives such as subsidies and payments to encourage family-building. In 2021, the policy was further relaxed to allow couples to have up to three children. However, these initiatives have seen limited success, with economic factors and changing societal priorities emerging as deterrents to family expansion.
Impact of Economic Pressures: Cost of Living and Career Priorities
Young people in modern Chinese cities, particularly those who weathered the economic challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic, cite deterrents such as the high cost of living and career priorities as significant barriers to starting families. Wang Chengyi, a 31-year-old woman in Beijing, expressed the financial challenges, stating, “My husband and I do want to have a kid, but we can’t afford it for now.” She highlighted the need to save money for several years to meet the expenses associated with raising a child.
Pandemic’s Role: Accelerating the Decline in Births
Experts acknowledge the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in accelerating the decline in new births. However, they emphasize that underlying economic issues, including the struggles faced by the Chinese economy in 2023, play a more substantial role in shaping demographic trends.

Economic Struggles: Property Crisis and Youth Unemployment
China’s Population economic challenges came to the forefront in 2023, marked by a widespread property crisis, falling consumer spending, and record youth joblessness. Annual data confirmed the struggles, with GDP expanding at 5.2% to reach 126 trillion yuan in 2023, the slowest rate since 1990, excluding the pandemic years. The youth unemployment rate for December stood at 14.1%, reflecting the economic pressures faced by the younger population.
Aging Workforce and Economic Concerns
China’s Population reliance on an aging workforce as a key driver of its economy raises concerns about healthcare and pension systems. The retiree population is projected to increase by 60% to 400 million by 2035, placing additional strain on these systems. Despite these challenges, experts suggest that China, like other deindustrializing countries, has the time and resources to manage the transition in its workforce.
Government Response: Planned Direction for Economic Shift
Experts note that China’s Population is following the pattern of other nations that have deindustrialized rapidly. The government has been proactive in planning for this shift over the past decade, anticipating a more educated, skilled, and healthier population desiring different jobs than traditional factory or construction work. While the economic challenges persist, the government’s awareness and planning position China to navigate this transition effectively.
Conclusion: China’s Demographic Crossroads
China, once the most populous nation globally, now faces a demographic crossroads with a second consecutive year of population decline. Economic factors, societal priorities, and the aftermath of the pandemic contribute to a complex landscape. As the government strives to address these challenges and manage the impact on its workforce and economy, the coming years will be crucial in shaping China’s demographic and economic future.

